This post was originally published on this site
Inflation surged in June, but it is now at or near its peak for this cycle.
What will determine the path of consumer-price inflation from this point on is how companies answer a key question: What is more important, protecting profit margins or protecting market share?
There is no doubt that input costs have soared. Paying higher wages to attract new workers and retain current employees does raise operating expenses. So does spending more on key commodities. The temptation therefore to pass those higher costs on to customers is strong.
Calculated risk
But it is also a calculated risk. There is always the fear that longtime clients will walk away and instead do business with a competitor who suddenly sees an opportunity to stand out from the pack by dropping prices. And if there is one painful lesson companies of all sizes have learned it is that once you lose market share, it is hellishly difficult and expensive to get it back.
What June’s 0.9% jump in the consumer price index tells us is that most businesses found their operating expenses increased way too much and way too quickly to simply be absorbed. They had to make up for those shrinking margins by charging consumers more.
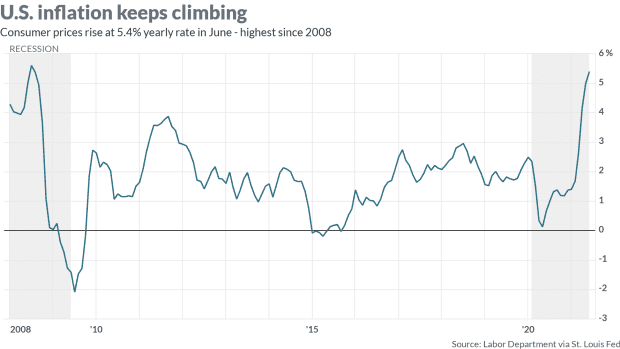
Again, it’s a calculated risk and probably a safe one…for now! After all, households are flush with cash and eager to spend, and that means Americans are less likely to be price sensitive at this time. We haven’t seen such pricing power in decades. Inflation has risen by 5.4% over the past 12 months, the fastest gain since the summer of 2008, with core CPI up a sharp 4.5%, the most since 1991.
So long as pricing power doesn’t threaten market share, inflation will continue to creep higher. But history has shown this cannot last long. Price competition will re-emerge in the second half of the year and more vigorously in 2022 and that should soften inflation pressures. Here’s why.
Here’s why inflation has peaked
First, as Washington transitions from fiscal stimulus to fiscal restraint, we expect to see household consumption ease accordingly.
Second, the enormous buildup in pent-up demand by consumers over the past year provided the economy with much forward momentum. But as demand is being satisfied, this spending drive will lose momentum.
Third, there is little doubt the Federal Reserve is gearing up to scale back purchases of mortgage-backed securities and Treasuries. Whether it begins to taper quantitative easing at the end of this year or early next, once they do, the cost of borrowing will increase. That will slow both home sales and capital investments.
Fourth, the supply-chain bottlenecks of the first half have begun to ease. Cargo ships are being unloaded at a faster pace, especially on the West Coast. This improvement in logistics sets the stage for the price of commodities and finished goods to drift lower.
Finally, and I say this will some reluctance, as much as we wish to declare victory over the COVID-19 virus, it would be premature to do so. The appearance of new variants (Delta, Delta plus and now Lambda) in the U.S., combined with the challenge of getting 70% to 80% of the U.S. population fully vaccinated (the figure is only 48% as of today, according to the CDC) raises the specter of another wave of infections in the fall and winter. That, too, could also take some wind out of the economy.
Our assessment is we are near the peak in the inflation cycle and most voting members on the Federal Open Market Committee share this general sentiment. The forces that drive price competition and bring down retail prices are bound to emerge as consumers seek out more deals and as firms refocus on locking in, if not expanding, their market share.
Bernard Baumohl is chief global economist for The Economic Outlook Group.
More on the CPI report
The cost of living posts biggest surge since 2008, CPI shows, as inflation spreads through economy
Fed’s Daly says the strong June inflation reading was expected and higher prices won’t last
Why used-car prices are driving U.S. inflation higher
U.S. stocks hover near records after hot CPI data, as big banks kick off earnings season

